- 80862_npc_final_cr206feb15.pdf2.15 MB
/ MEDIA STATEMENT / The content on this page is not written by Polity.org.za, but is supplied by third parties. This content does not constitute news reporting by Polity.org.za.
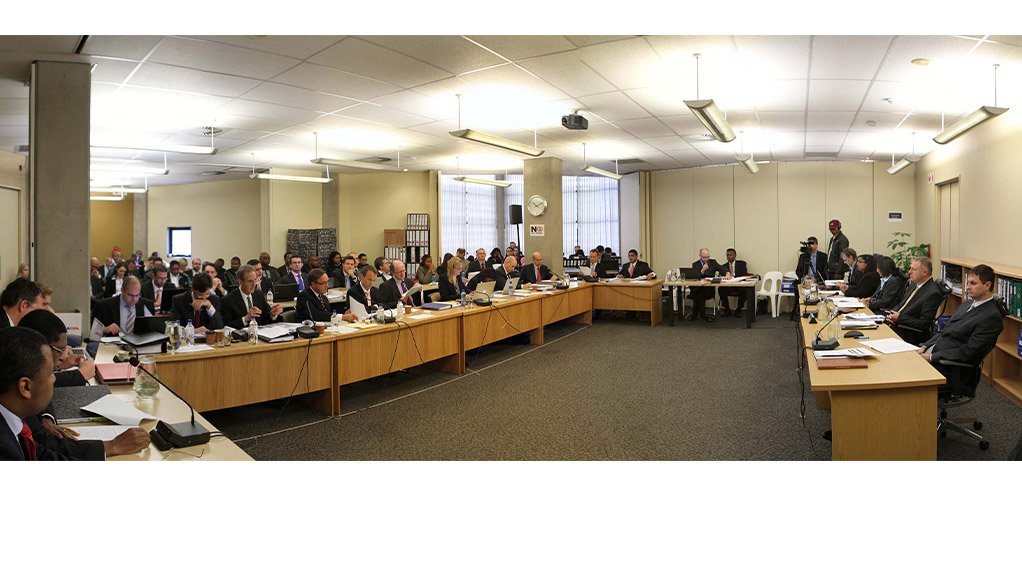
A decade after the Competition Commission launched its investigation into a cement cartel, the matter has now been finalised with the Competition Tribunal dismissing a case of indirect price fixing and market division against Natal Portland Cement Cimpor (Pty) Ltd (NPC).
Background
The cement industry cartel case stemmed from a Competition Commission investigation launched in 2008, which probed alleged anti-competitive conduct in the cement industry in South Africa. This was against a backdrop of meetings held in exclusive venues as far afield as Paris and Portugal as well as agreements stemming from the various meetings held both locally and abroad.
The allegations that NPC, Pretoria Portland Cement Company Limited (PPC), Lafarge Industries South Africa (Lafarge) and AfriSam Consortium (Pty) Ltd (AfriSam) had engaged in cartel conduct between 1995 and 2009 culminated in the Commission raiding the companies’ offices a year later in 2009.
PPC
PPC subsequently admitted to being part of the cartel and was granted conditional leniency (immunity from prosecution) in terms of the Commission’s Corporate Leniency Policy, in exchange for it helping the Commission to prosecute the remaining cartel members.
The Commission alleged, among others, that the companies had agreed in 1995 to allocate each cement producer the market share it had held before 1996 when a lawful cement cartel existed under apartheid – and that the cartel had agreed to collude and divide up cement markets in South Africa, Lesotho, Botswana, Swaziland and Namibia (the Southern African Customs Union region).
The Commission also alleged that a second agreement was reached in 1998, refining the 1995 agreement and reallocating market shares. This so-called “Port Shepstone Agreement” was the main thrust of the Commission’s case against NPC.
Afrisam and Lafarge
Evidence had emerged during the hearing before the Tribunal that the global consulting firm, McKinsey and Company had advised Afrisam in 1998 to cartelise by cooperating with competitors through a strategy known as co-opetition. This formed part of an admission in a witness statement by a former AfriSam Managing Director, who has since died. McKinsey had denied his claims.
The Tribunal had also heard evidence that Lafarge executives had summonsed the newly appointed MD of its South African subsidiary to a Paris meeting in 1998 – a time when the local subsidiary’s market share had dropped -- where he was instructed to explain “global rules” of the cement industry to other cement producers in South Africa.
Both AfriSam and Lafarge had admitted to contravening the Competition Act. AfriSam had agreed to settle with the Commission in 2011 and paid an administrative penalty (a fine) of R124 878 870. Lafarge also settled and paid a fine amounting to R148 724 400 in 2012.
Both Afrisam and Lafarge had also agreed to cooperate with the Commission in its pursuit of the case against NPC. This meant NPC was the only company left facing the allegations.
NPC
The three cement companies had been equal shareholders in NPC until 2002. NPC, however, denied that it had contravened the Competition Act or that it was liable to pay an administrative penalty. The Commission referred the case against NPC to the Tribunal for prosecution in 2015.
The company denied the Commission’s allegations that it had been party to anti-competitive arrangements and meetings – including a meeting in Lisbon, Portugal, in 2002 between Lafarge and NPC executives which allegedly culminated in an agreement to give NPC an advantage in KwaZulu-Natal.
Tribunal order and reasons
The crux of the Commission’s case is that the cement companies, following a price war which was devastating for the producers, held a series of meetings which culminated in a 1998 meeting held in Port Shepstone. The Commission argued that a consensus was reached at that meeting which constituted a cartel that included NPC.
In its order and reasons the Tribunal says: “While it is true that a reasonable suspicion may exist that Strauss [NPC] played a greater role at the Port Shepstone meeting than may appear at first blush and that he may have involved NPC in cartel arrangements, the facts don’t adequately support such a suspicion… Mr Strauss’ actions post the takeover of NPC by Cimpor are hardly indicative of a person either involved in cartel arrangements or trying to maintain those arrangements.”
The Tribunal continues: “It is common cause that PPC, Lafarge and Afrisam had reached consensus on maintaining market stability according to the international cement rules and that the price war engaged in by the three had hurt them financially. The Port Shepstone agreement resolved those issues amongst the three of them. NPC was never involved in the price war. There was no need for it to get so involved. It was operating at maximum capacity which it could not increase and operated mainly, almost exclusively, in Southern KwaZulu-Natal where the others had only a limited presence and where selling cement at competitive prices was challenging because of the transport costs in doing so…
It is reasonable to accept that NPC had no interest in the discussions which were held by the others and explains why Mr Strauss was in and out of the meeting and felt no need to report on the meeting to NPC staff members. Under those circumstances it could not be said that NPC was a party to that agreement.”
“NPC took steps to expand its capacity after the takeover by Cimpor. Prima facie that was inconsistent with a capacity-based market sharing agreement. The expansion did take some time, but the steps taken were outlined by Mr Strauss and his evidence was never contradicted by other witnesses.”
In dismissing the Commission’s complaint against NPC-Cimpor, the Tribunal concludes: “… The discussions between Lafarge, Afrisam and PPC centered around the allocation of their market shares, transport costs and profits and not NPC’s.”
Full Details Attached
Issued by The Competition Tribunal
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE ARTICLE ENQUIRY
To subscribe email subscriptions@creamermedia.co.za or click here
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here