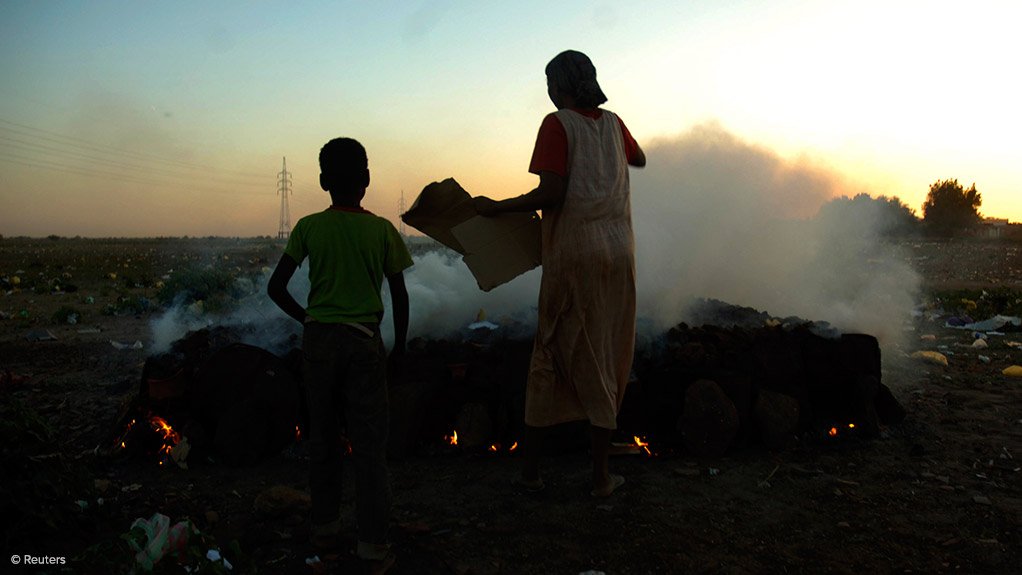
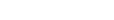In a nutrition ward at a hospital in Sudan's war-stricken capital, gaunt mothers lie next to even thinner toddlers with wide, sunken eyes.
The patients at Alban Jadeed Hospital are in urgent need of help after nearly two years of battles that have trapped residents and cut off supplies, but doctors have to ration the therapeutic milk and other products used to treat them.
The war that erupted in April 2023 from a power struggle between Sudan's army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) has created what the United Nations calls the world's largest and most devastating humanitarian crisis.
About half of Sudan's population of 50-million now suffer some degree of acute hunger, and famine has taken hold in at least five areas, including several parts of North Darfur State in western Sudan.
The real situation could be worse, since fighting has prevented proper data collection in many areas, medics and aid staff say.
In Sudan's greater capital, where the cities of Khartoum, Omdurman and Bahri are divided by the Nile, the warring factions have prevented deliveries of aid and commercial supplies, pushing the prices of goods beyond most people's reach.
Alban Jadeed Hospital, in Bahri's Sharg Elnil district, received more than 14 000 children under five years old suffering from severe acute malnutrition last year, and another 12 000 with a more mild form, said Azza Babiker, head of the therapeutic nutrition department.
Only 600 of the children tested were a normal weight, she said.
The supply of therapeutic formula milk via UN children's agency UNICEF and medical aid agency MSF is insufficient, Babiker said, as RSF soldiers twice stole the supplies.
Both sides deny impeding aid deliveries.
The sharp reduction of USAID funding is expected to make things worse, hitting the budgets of aid agencies that provide crucial nutritional supplies as well as community kitchens relied upon by many, aid workers say.
The army recently captured Sharg Elnil from the RSF, as part of recent gains it has made across the capital.
Fruit and vegetables have become extremely scarce. "Aside from the difficulty of getting these products in, not all families can afford to buy them," Babiker said.
Many mothers are unable to produce milk, often due to trauma resulting from RSF attacks, or their own malnutrition, said Raneen Adel, a doctor at Alban Jadeed.
"There are cases who come in dehydrated ... because for example the RSF entered the house and the mother was frightened so she stopped producing breast milk, or she was beaten," she said.
The RSF did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
A lack of nutrition and sanitation has led to cases of blood poisoning and other illnesses, but the hospital has also run out of antibiotics.
"We had to tell the patients' companions to get (the drugs) from outside, but they can't afford to buy them," Adel said.
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE
To subscribe email subscriptions@creamermedia.co.za or click here
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here