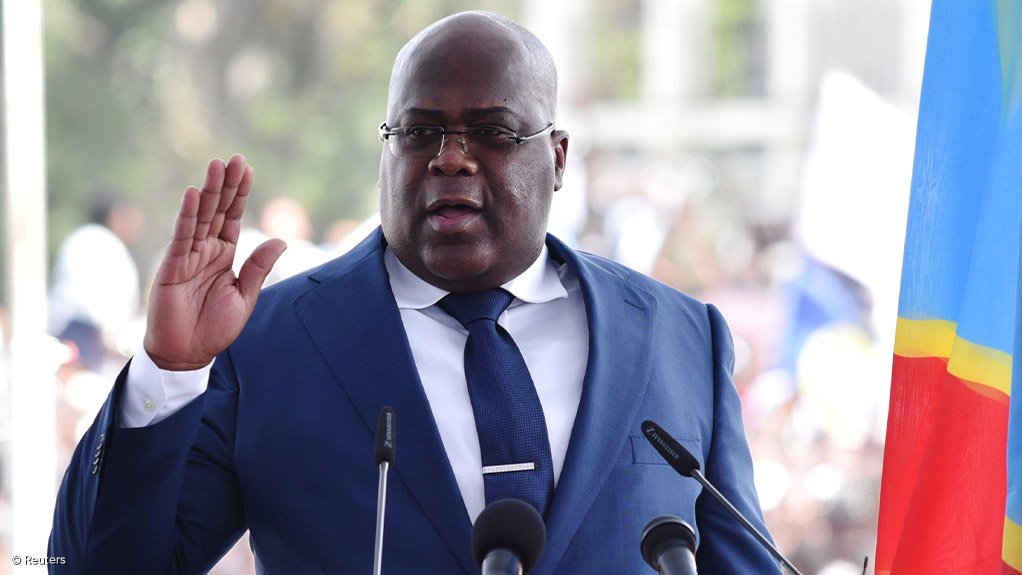
Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) President Felix Tshisekedi has long ruled out dialogue with the Rwanda-backed M23 rebels rampaging through eastern parts of his country, but a string of defeats and waning regional support have forced him think again.
Neighbouring Angola caught many by surprise this week by saying Congo and M23 would sit down for direct talks in its capital on March 18, at a time when the rebels are still seizing territory rich with coltan, tantalum and other minerals.
Tshisekedi's government has so far not committed publicly, but three government sources told Reuters this week he was seriously considering sending a delegation.
With Congo's army and allied forces putting up weak resistance to the rebel advance, regional powers appear in agreement that dialogue is the only way forward, diplomats and analysts said.
"I haven't talked to a single African country that says Kinshasa shouldn't talk to M23," one senior diplomat said.
"The line of everyone is, 'How do you stop the fighting if you don't engage with them?'"
One source said on Friday that government participation was a sure thing but that it was still too early to say who would represent Kinshasa in Luanda.
Other sources said the debate was still ongoing and that a final decision was not likely to be made until next week.
M23, for its part, said on Thursday it was demanding an unequivocal commitment from Tshisekedi to engage in talks.
Both sides said they had questions about the framework and how the Angola-hosted talks would comply with decisions from regional bodies attempting to resolve the conflict.
Southern and East African foreign and defence ministers are due to meet in Harare on Monday to discuss the push for a cessation of hostilities and political dialogue.
'FAILED' MILITARY APPROACH
M23 is backed by thousands of Rwandan troops, according to UN experts, and their superior weaponry and equipment has allowed them to seize east Congo's two biggest cities since late January along with a host of smaller localities.
Rwanda denies providing arms and troops to M23, and says its forces are acting in self defence against the Congolese army and militias hostile to Kigali.
Sitting down with M23 would likely be deeply unpopular in Kinshasa, especially after Tshisekedi's repeated vows never to do so.
But it would amount to an acknowledgment that Tshisekedi's pursuit of a military solution has "failed", said Congolese analyst Bob Kabamba of the University of Liege in Belgium.
"Kinshasa's position of dialogue is understandable because it finds itself stuck, thinking that the (rebel alliance) must not reach a critical threshold," he said.
Congo's neighbour Angola may have made a similar calculation, wary of being drawn into a larger-scale regional war reminiscent of those that killed millions in the 1990s and early 2000s.
"Angola has clearly decided that it is necessary to intervene to prevent the advance of the M23 towards the west of the DRC," said Stephanie Wolters, a Congo analyst with South Africa's Institute for Security Studies.
The lack of faith in Tshisekedi's ability to turn the tide militarily was also seen this week in Southern African leaders' approval of the "phased withdrawal" of a regional deployment known as SAMIDRC that had a mandate to fight rebels.
Although the deployment was too weak to mean much in the fight against M23, its presence was an important sign of regional support for Congo, Wolters said, making its departure a "significant blow".
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE
To subscribe email subscriptions@creamermedia.co.za or click here
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here